Basilisk
Basiliscus basiliscus is the latin name of the extraordinary Jesus Christ lizard, famous for its ability to run on the surface of water, a characteristic it shares with another well-known water-walker Gerris lacustris.
Basilisk is also the name of a Free Software program for the solution of partial differential equations on adaptive Cartesian meshes. It is the successor of Gerris and is developed by the same authors.
If you want to find out more about Basilisk see:
- Tutorial
- Installation instructions
- Basilisk C
- Solvers and functions
- Examples
- Tests
- More documentation
Picture of the month
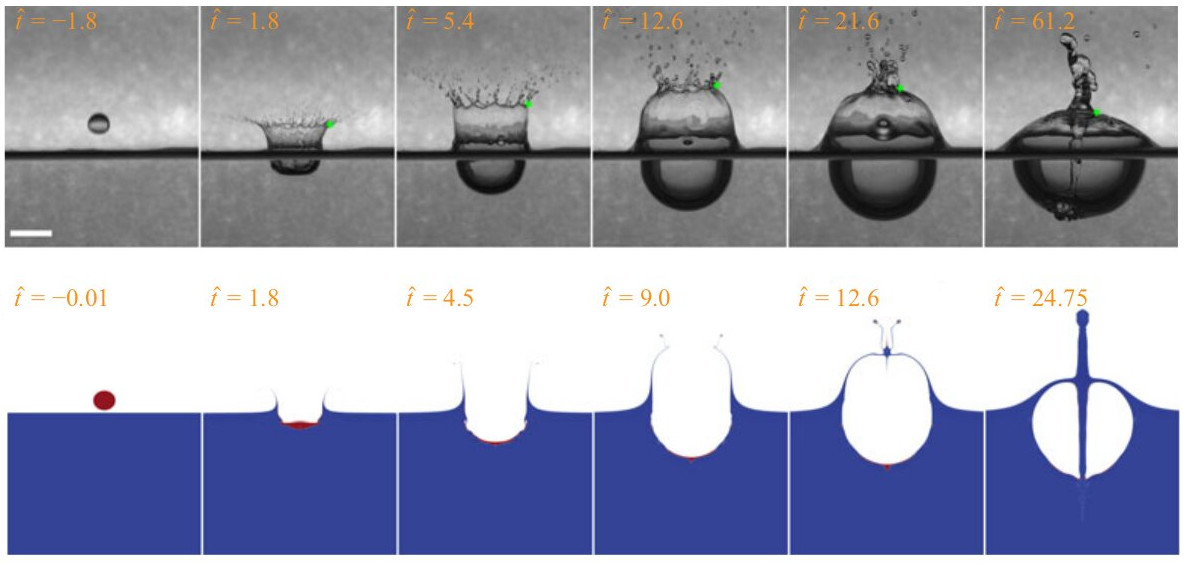
See also the POM Gallery.
News
Next Basilisk Monthly Meeting: Tuesday, October 28th, 4pm CET
Recent publications (see Bibliography for more).
| [boniou2025] |
Victor Boniou, Stephane Jay, Guillaume Vinay, and Jean-Lou Pierson. Collision statistics of finite-size monodisperse droplets in homogeneous isotropic turbulence. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1020:A18, October 2025. [ DOI ] |
| [long2025] |
Tian Long, Jieyun Pan, Edoardo Cipriano, Matteo Bucci, and Stéphane Zaleski. Direct numerical simulation of nucleate boiling with a resolved microlayer and conjugate heat transfer. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1020:A30, October 2025. [ DOI ] |
| [lemarechal2025] |
Cyprien Lemaréchal, Guillaume Roullet, and Jonathan Gula. Hydrothermal Plume Near-Field Dynamics From LES and Observations. Journal of Geophysical Research. Oceans, 130(10):e2024JC022277, October 2025. [ DOI | http | .pdf ] |
| [grea2025] |
Benoit-Joseph Gréa, Andrés Castillo-Castellanos, Antoine Briard, Alexis Banvillet, Nicolas Lion, Catherine Canac, Kevin Dagrau, and Pauline Duhalde. Frozen waves in the inertial regime. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1021:A12, 2025. [ DOI | http | .pdf ] |
